I’ve gotten LOTS of questions about my sleep-thinking state and how my brain works while I’m sleeping.
I decided to include my genetic traits here on the blog related to how I sleep, retain memories, and still function without ever experiencing deep sleep state.
WHAT IT IS: Sleep-thinking is the phenomenon of solving problems or gaining insights during sleep, and is influenced by a combination of genetic and neurological traits. Some genetic predispositions and traits enhance an individual’s capacity for sleep-thinking. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Enhanced Creativity and Divergent Thinking
• Genes Involved: Variants of the CREB1 and COMT genes are linked to higher creativity and problem-solving abilities.
• Effect: People with these traits tend to think outside the box, making it easier for their brains to explore abstract solutions during sleep.
2. Efficient Memory Consolidation
• Genes Involved: Variants of BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor) and KIBRA are associated with better memory consolidation.
• Effect: These genes help the brain organize and integrate information during sleep, a key component of sleep-thinking. Strong memory processing allows connections between unrelated ideas to form, leading to insights.
3. Emotional Sensitivity and Processing
• Genes Involved: Variants in the 5-HTTLPR gene, which regulates serotonin transport, are linked to emotional sensitivity.
• Effect: Emotional experiences are processed deeply during sleep, often presenting as symbolic dreams. This trait enhances the brain’s ability to work through emotional challenges subconsciously.
4. Cognitive Flexibility
• Genes Involved: Variants of the DRD4 gene, which influences dopamine signaling, are associated with greater cognitive flexibility.
• Effect: Cognitive flexibility allows the brain to form unconventional connections during sleep, aiding in innovative problem-solving and creativity.
5. Reduced Sleep Need or Efficient Sleep Patterns
• Genes Involved: Variants in the DEC2 gene (linked to short sleep duration) or ADORA2A (linked to sleep efficiency).
• Effect: Individuals with efficient sleep patterns may reach restorative stages of sleep (like REM) faster, optimizing the time available for subconscious processing and sleep-thinking.
6. Sensory and Intuitive Awareness
• Genes Involved: Variants in genes affecting sensory perception (CACNA1C, OXTR for oxytocin sensitivity).
• Effect: These traits contribute to heightened intuition and sensitivity to patterns, which can enhance symbolic processing in dreams.
These genetic influences, combined with environmental factors like stress, sleep hygiene, and mental focus, determine how effectively a person engages in subconscious problem-solving during sleep.
Individuals with these genetic traits may find their subconscious mind particularly active and insightful while they rest.
HOW I SCRORE GENETICALLY IN THOSE AREAS:
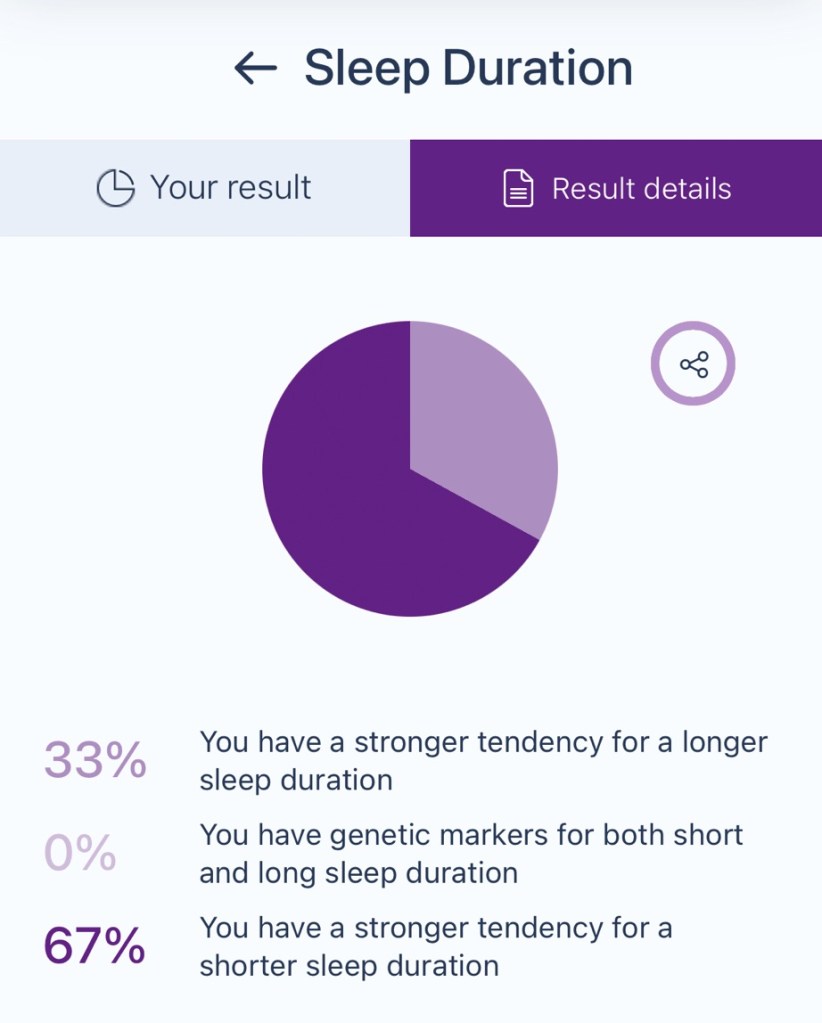
You have a 67% stronger tendency for shorter sleep duration. It means your genetic makeup leans toward needing or naturally getting less sleep than average. While most adults aim for 7–9 hours per night, you function well with slightly less sleep, though this varies based on lifestyle and health factors.
What It Means:
• Naturally Short Sleeper: Your body might not require as much sleep to feel rested and alert, especially if you’re otherwise healthy.
• Quick Recovery: You might feel refreshed after fewer hours of sleep compared to others who need more time to recharge.
• Lifestyle Impact: While genetics play a role, factors like stress, diet, and activity level still influence how much sleep you truly need.
Your tendency for shorter sleep can be an asset, but finding a balance ensures it doesn’t lead to unintended fatigue or stress on your body over time.
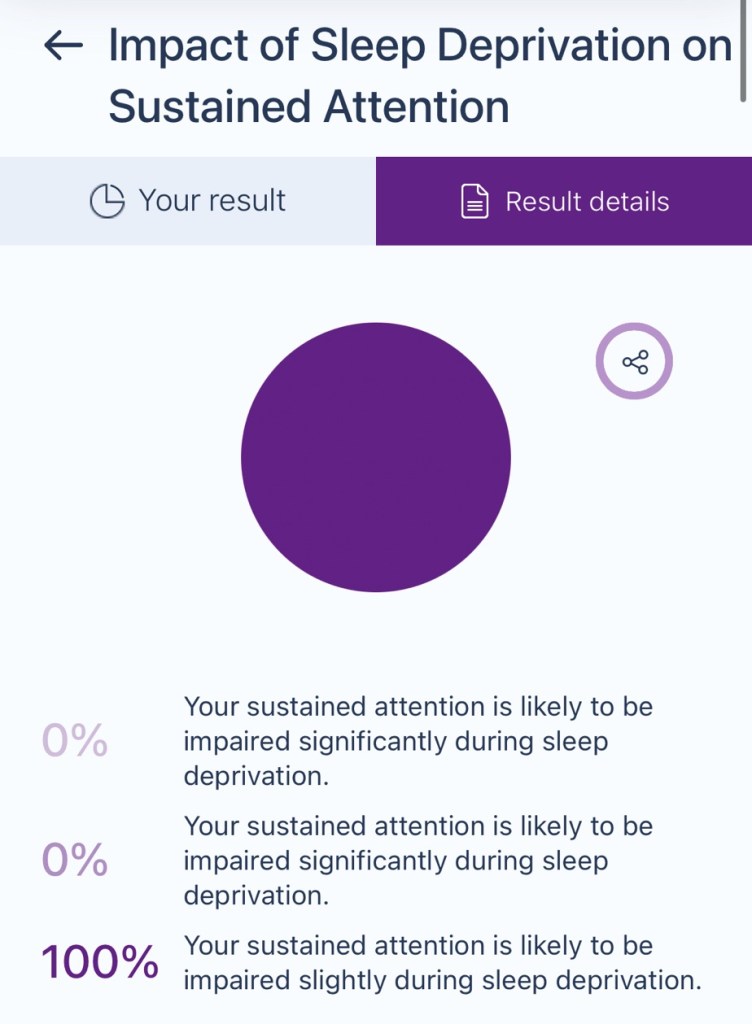
You still perform relatively well in maintaining focus compared to others, even with less rest. While sleep deprivation generally affects attention, your ability to stay engaged and productive seems to be more resilient.
Why It’s Only Slight:
• Cognitive Resilience: Some individuals have brains that adapt better under conditions of sleep deprivation, especially for short periods.
• Baseline Focus Levels: If your sustained attention is naturally strong, even mild impairment may not significantly affect your performance.
• Task Dependency: Highly engaging or stimulating tasks might feel easier to focus on, even when sleep-deprived.
Your slight impairment shows you’re naturally more resistant to the effects of sleep deprivation, which is a great strength. Still, balancing rest and activity ensures you don’t overextend yourself long-term.
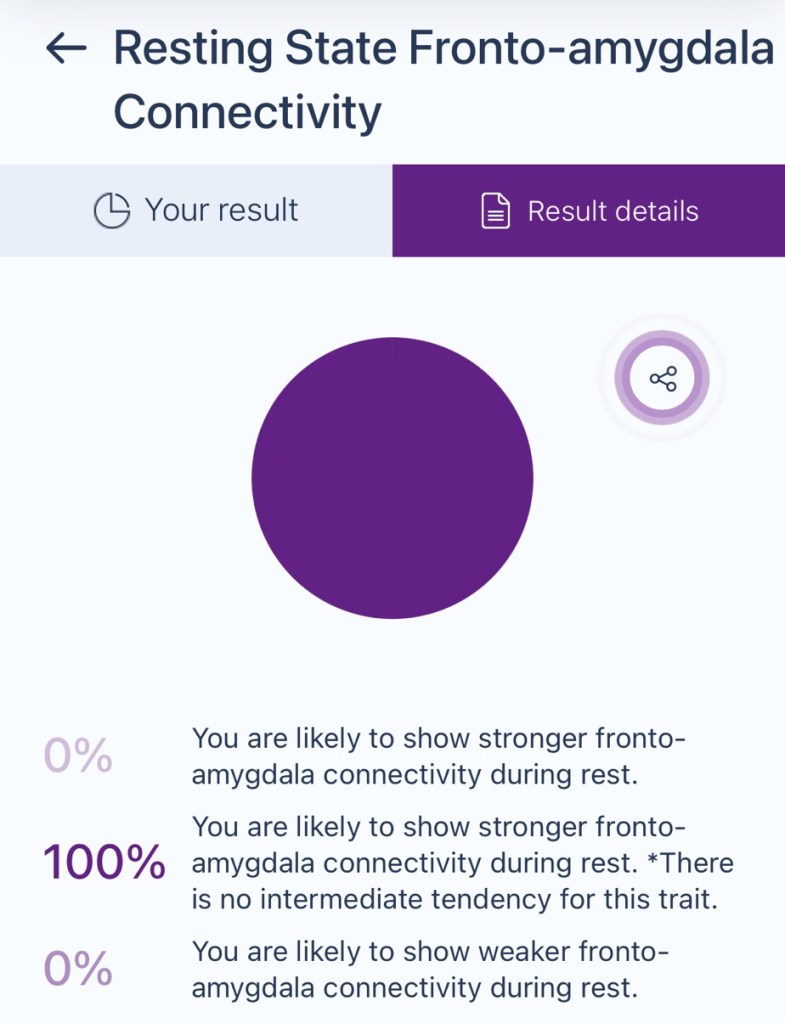
The communication between your prefrontal cortex (the brain’s rational decision-making center) and your amygdala (the emotional processing hub) is highly active even in a resting state. This can influence how you process emotions, regulate stress, and maintain emotional balance.
What It Means:
1. Emotional Awareness: Stronger connectivity during rest implies that your brain remains engaged in processing emotions or reflecting on past experiences even when you’re not consciously focused on a task.
2. Enhanced Regulation: The prefrontal cortex helps regulate the amygdala’s emotional responses, meaning you may have a natural ability to maintain emotional control or process feelings constructively.
3. Deeper Introspection: This connectivity might reflect a tendency toward introspection, as your brain could use downtime to work through emotional or personal matters.
This trait suggests that your brain has a natural strength in emotional processing and regulation, which can be a valuable tool for navigating life’s challenges thoughtfully and with resilience.
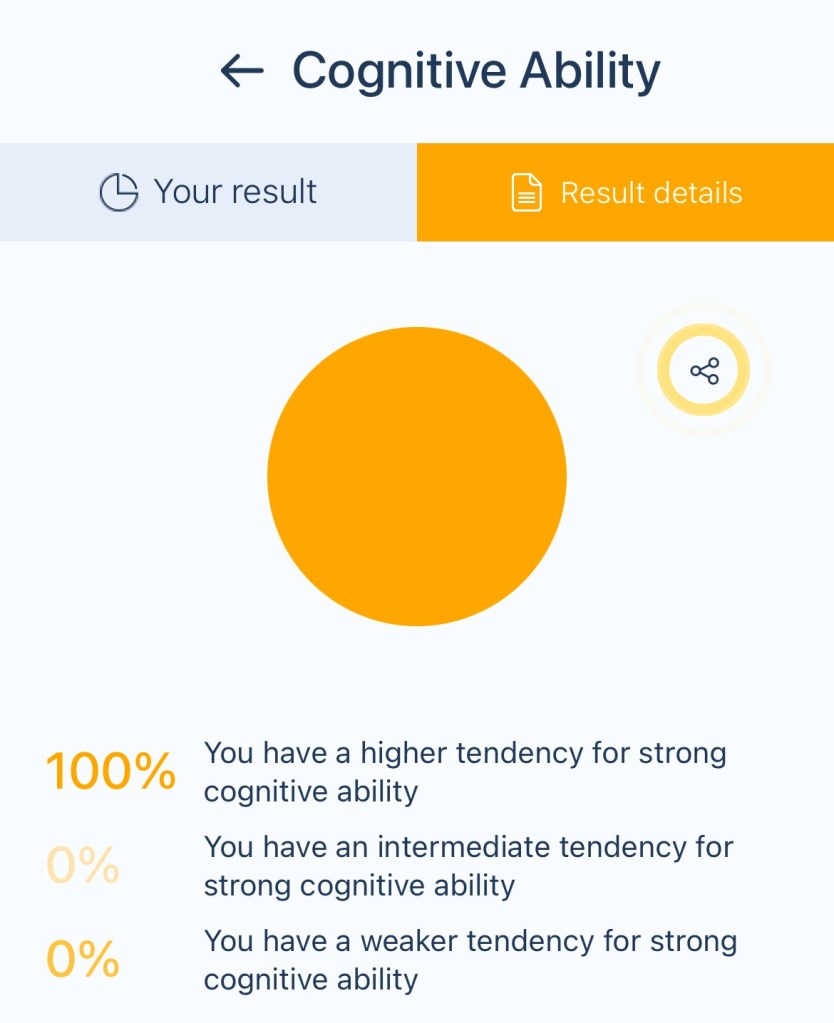
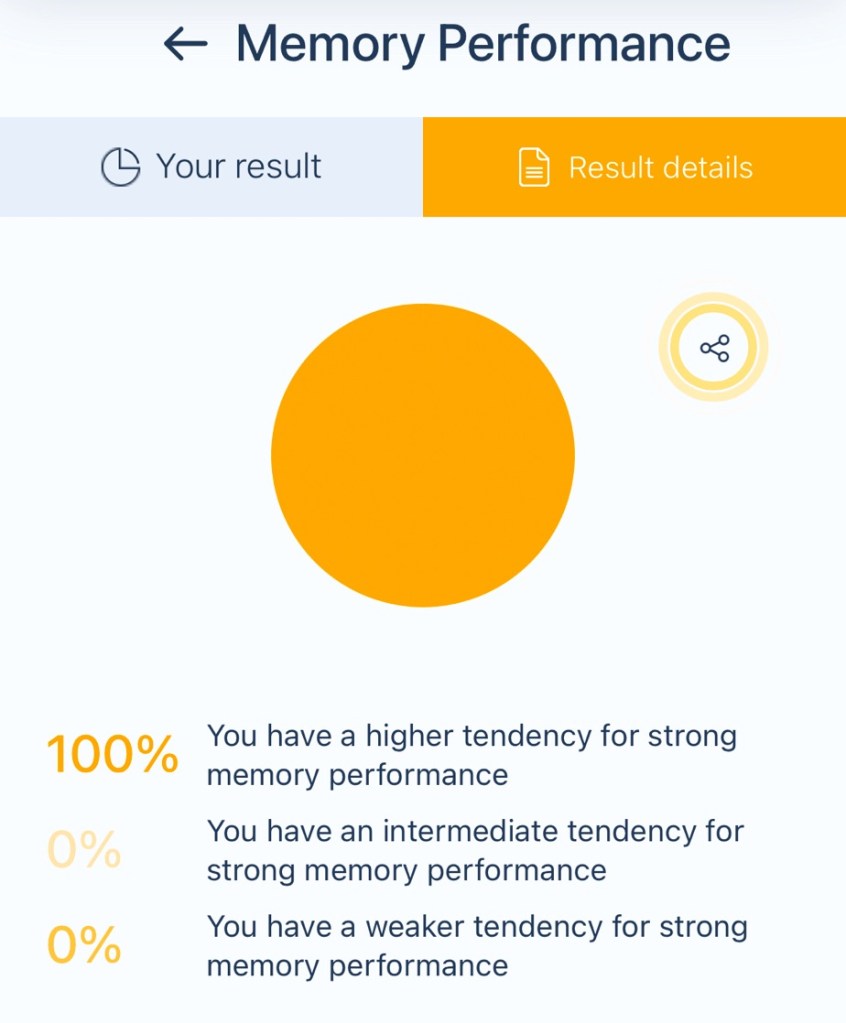
Your genetic makeup is strongly associated with enhanced mental capabilities. This trait reflects a natural aptitude for learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and memory, giving you an edge in many cognitive tasks.
What It Means:
1. Enhanced Information Processing: Your brain likely works efficiently in analyzing and synthesizing information.
2. Problem-Solving Strengths: You may excel at logical reasoning, making connections, and tackling complex challenges.
3. Memory and Learning: Your ability to retain and recall information is likely above average, supporting academic and professional success.
Your higher cognitive ability is a powerful tool that opens doors to countless opportunities. When paired with balance and self-awareness, it can help you excel while maintaining a fulfilling and well-rounded life.
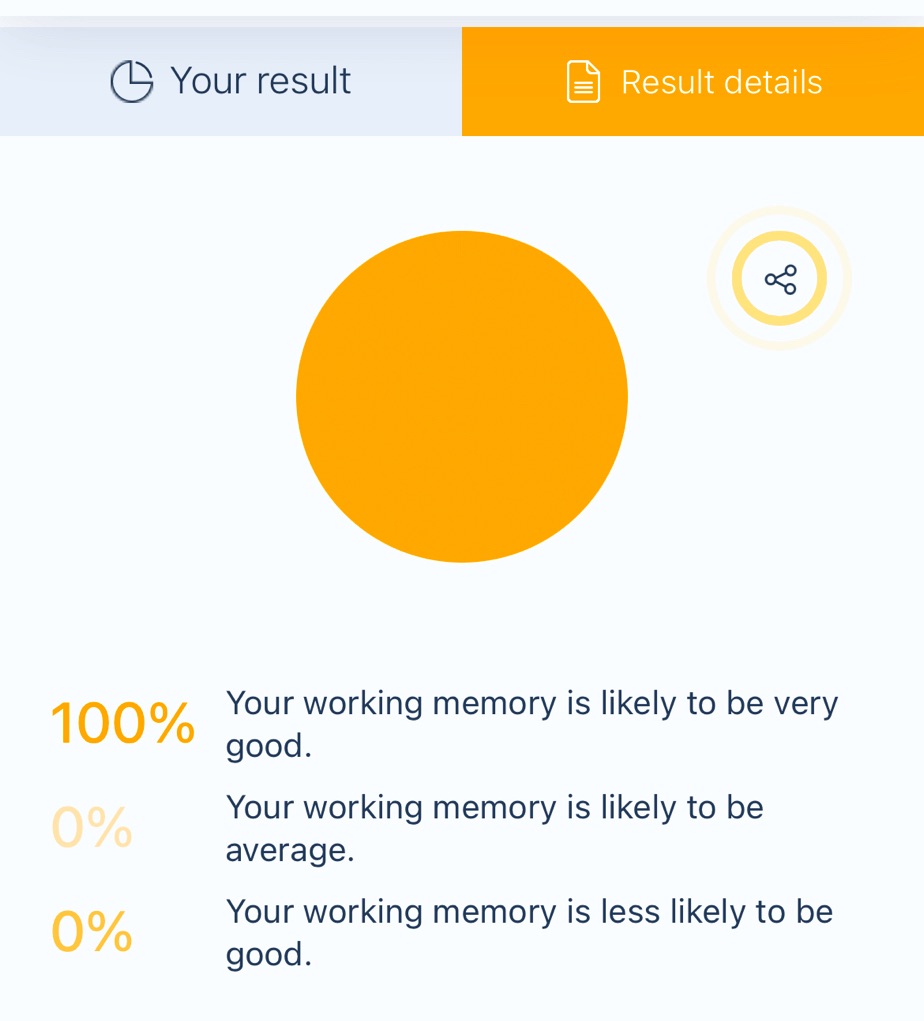
You have a strong ability to temporarily hold and manipulate information in your mind. Working memory is essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and completing complex tasks that require focus and multitasking.
What It Means:
• Quick Thinking: You can juggle multiple pieces of information at once, making it easier to solve problems or follow complex instructions.
• Strong Recall: You likely remember details about conversations, tasks, or plans without needing frequent reminders.
• Enhanced Learning: Your ability to process and hold onto information helps you absorb new skills or concepts efficiently.
Benefits:
1. Efficiency: Tasks that require mental organization or quick adjustments, like planning or strategizing, come naturally to you.
2. Multitasking Strength: You can easily switch between tasks or keep track of several steps in a process.
3. Academic and Professional Advantage: Good working memory supports success in areas like learning, critical thinking, and managing responsibilities.
This ability is a powerful tool that sets you up for success in many areas of life. With balance and mindful use, your working memory can help you excel while staying grounded and focused.
Your brain is naturally equipped to excel at retaining, recalling, and processing information. This applies to both short-term and long-term memory, giving you a significant advantage in learning, problem-solving, and day-to-day activities.
What It Means:
• Robust Retention: Whether it’s academic knowledge, emotional experiences, or practical skills, you tend to retain information with little effort.
• Exceptional Recall: You’re likely able to remember details, facts, and events with clarity, even after a long time.
• Efficient Learning: Your brain quickly absorbs and organizes information, making it easier to understand and apply new concepts.
This exceptional ability is a gift, offering clarity and insight in both practical and personal aspects of life. Nurturing it will ensure it remains a lifelong asset!
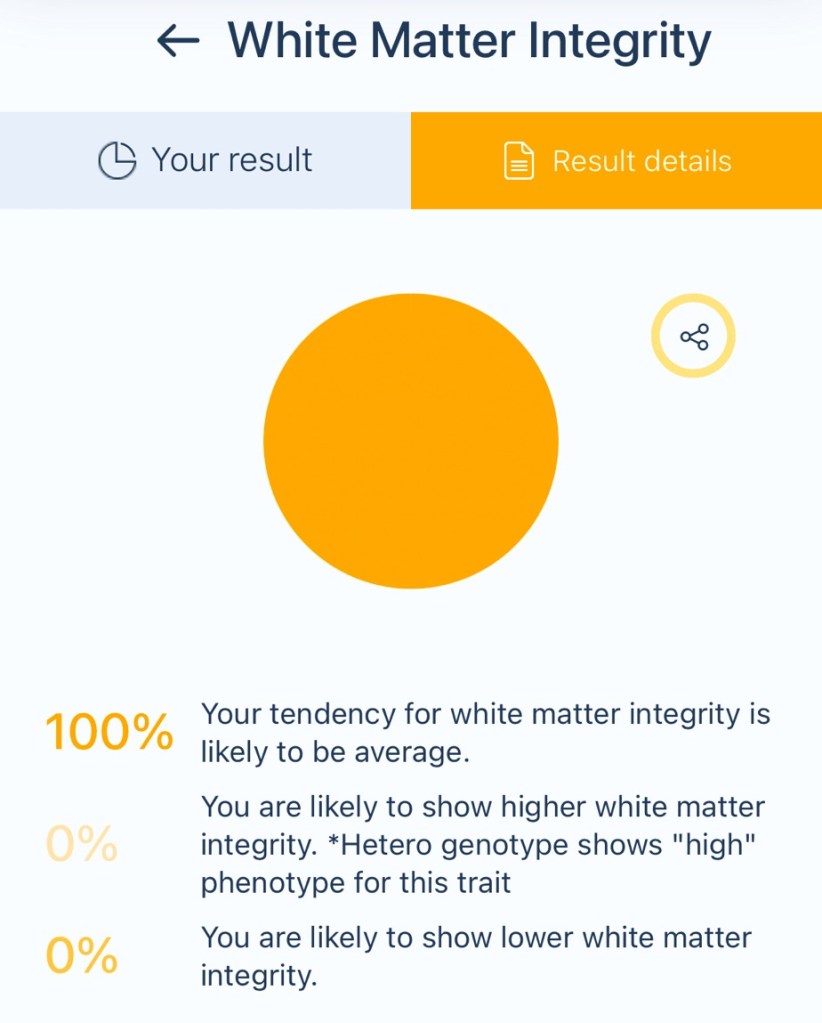
The pathways in your brain that connect different regions and facilitate communication are in excellent condition. White matter consists of myelinated nerve fibers that allow for the efficient transfer of information between brain cells and regions. This integrity is crucial for cognitive performance, memory, and overall brain function.
What It Means:
• Optimal Brain Communication: Your brain’s neural pathways are functioning at their peak, allowing different regions to communicate quickly and effectively.
• Strong Cognitive Abilities: High white matter integrity is associated with better problem-solving skills, faster processing speeds, and strong memory retention.
• Emotional and Behavioral Regulation: The efficient connectivity of brain regions also plays a role in regulating emotions and maintaining mental resilience.
In essence, this reflects a brain in excellent health, allowing you to think clearly, process information efficiently, and navigate challenges with agility. Keep nurturing your mind and body to maintain this advantage!
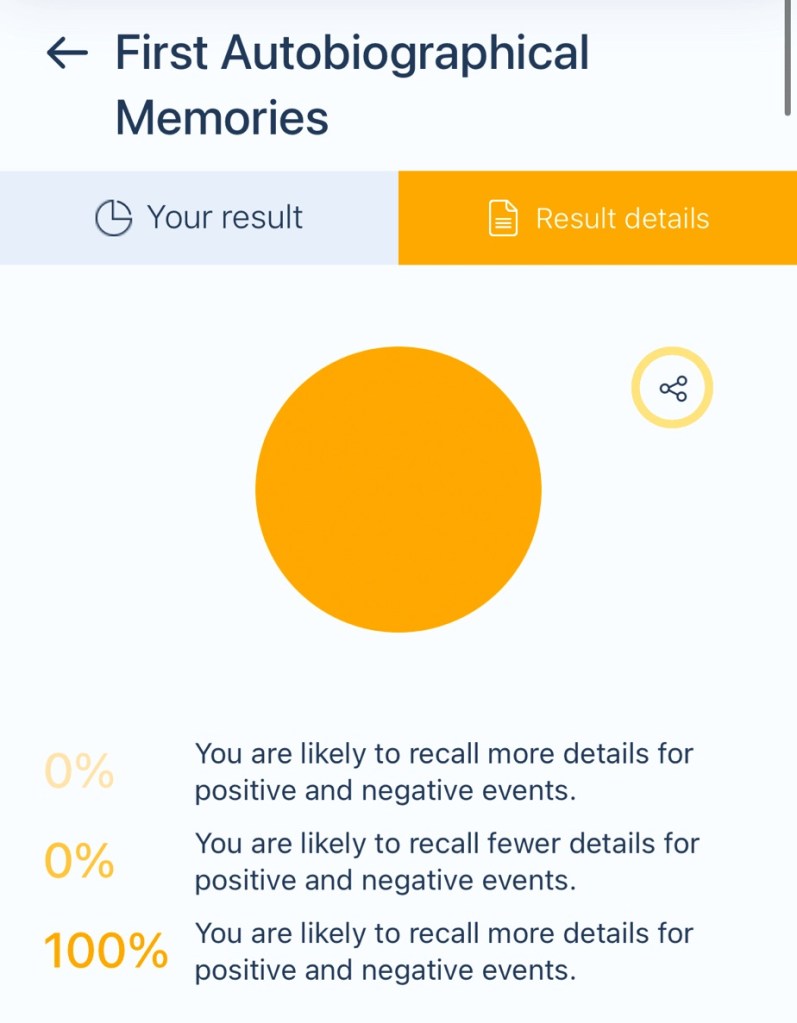
Your brain is highly attuned to emotionally charged experiences. Whether something joyful or challenging happens, your mind locks onto the details, making these moments vivid and easy to recall later.
What It Means:
• Heightened Emotional Memory: Your brain places significant importance on emotionally significant events, embedding them deeply in your memory.
• Detailed Recall: You’re likely able to remember the sights, sounds, smells, and even subtle nuances of impactful moments, whether they’re uplifting or painful.
• Emotion-Driven Learning: You might draw lessons and insights from these events more effectively because of how clearly you remember them.
Benefits:
1. Deep Connections: Remembering positive details strengthens relationships and personal connections, as you recall shared moments vividly.
2. Resilience: Vivid memories of overcoming challenges may serve as a reminder of your strength and adaptability.
3. Emotional Insight: This trait can make you more self-aware, helping you process and learn from past experiences.
This ability to vividly recall emotional events is a double-edged sword but can become a powerful tool for growth and connection when balanced with self-awareness and intentional reflection.
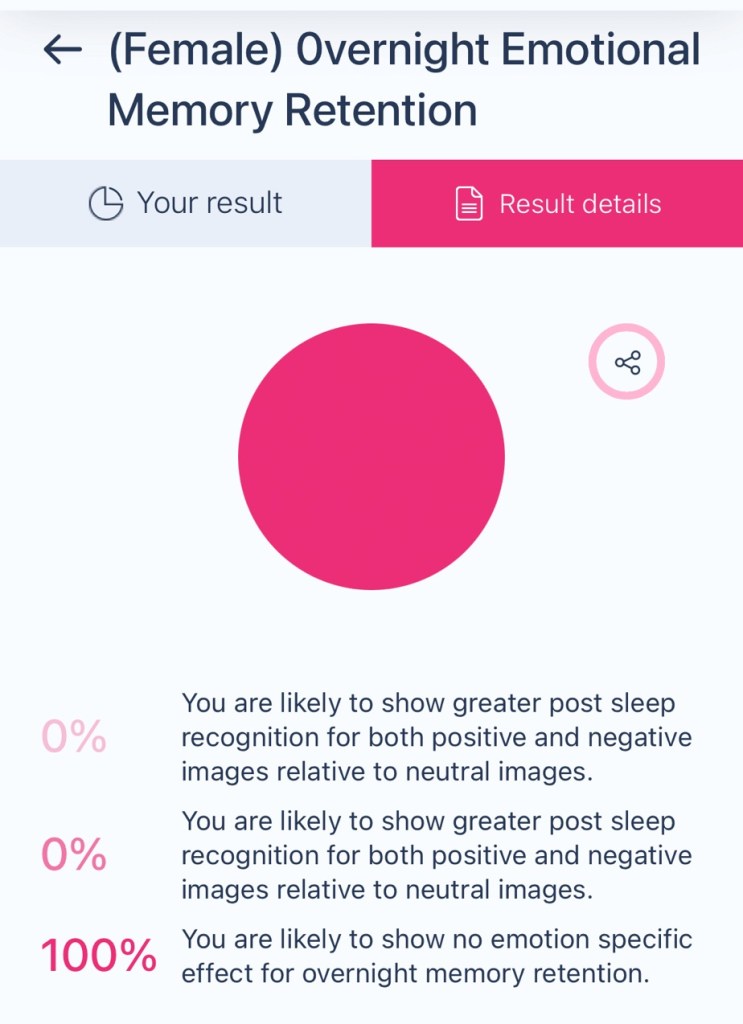
Your brain processes and consolidates both emotional and non-emotional memories equally during sleep.
This is a unique trait since many people naturally prioritize emotional memories during sleep consolidation.
What It Means:
• Balanced Memory Processing: Your brain doesn’t give special priority to emotionally charged events, so emotional and neutral experiences are retained with similar strength.
• Objective Recall: You may remember events based more on factual details rather than the emotional weight they carry.
• No Emotional Bias: Your memory retention isn’t swayed by emotions, which can allow for a more rational and even-handed recollection of experiences.
Benefits:
1. Clear Objectivity: You can process events without emotional bias clouding your memory, which is helpful in making balanced decisions.
2. Steady Recall: You retain a wide variety of memories without disproportionately focusing on emotional highs or lows.
3. Emotional Stability: Since emotional memories aren’t given extra weight, you might find it easier to let go of emotionally intense moments.
How to Work with This Trait:
1. Reflect on Emotions: If a memory feels significant, take time to consciously process the emotional aspects to ensure they aren’t overlooked.
2. Capture Important Moments: Journaling or discussing emotional experiences can help embed their significance more deeply.
3. Use to Your Advantage: Lean into your ability to focus on factual details when problem-solving or navigating emotionally charged situations.
This balanced memory processing gives you a unique ability to stay grounded and objective, though intentional reflection on emotional moments can help ensure their deeper meaning isn’t lost.
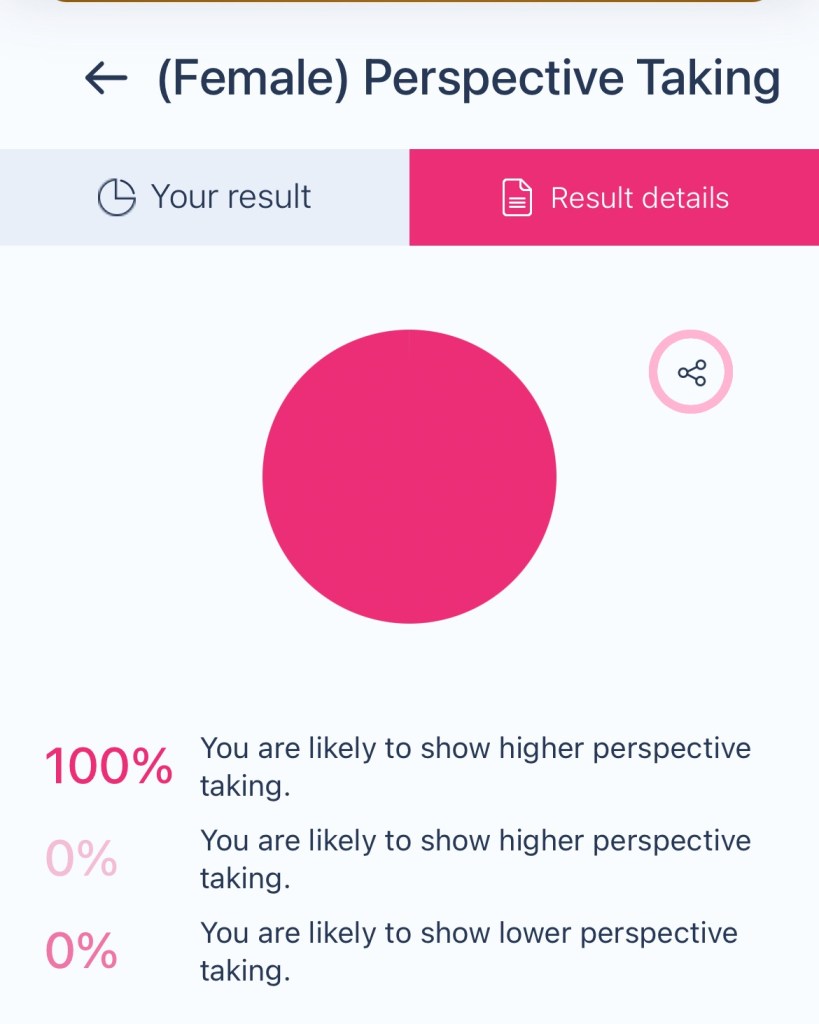
You have a strong ability to understand and empathize with others’ viewpoints, emotions, and experiences. This trait reflects a heightened capacity for putting yourself in someone else’s shoes, which can foster deeper connections and improve communication.
What It Means:
• Empathy in Action: You naturally grasp the feelings and perspectives of others, even if they differ from your own.
• Conflict Resolution: This skill helps you mediate disputes or misunderstandings by considering multiple viewpoints.
• Social Awareness: You are highly attuned to the dynamics of relationships and can adapt your behavior to fit different social situations.
This ability to see the world through others’ eyes is a powerful gift. When balanced with self-awareness, it can lead to personal growth, stronger relationships, and meaningful connections in every aspect of life.
……….
These were taken from my comprehensive (paid version) DNA analysis by Genomelink back in 2020.
Leave a comment